CONTENT LIST
Atoms
Atom is the smallest particle of element. Which cannot be broken / split up further by any physical or chemical process.
The concept of divisibility of matter was given in India by Maharshi Kanad around 500 BC.He called the smallest particle of matter as parmanu.
Atoms are the building block of matters.
Atoms are normally exist in a combined form which gives us various forms of matter.
Atomic radius is measured in terms of nanometres.
Dalton’s atomic theory
- All matter is made of very tiny particles called atoms.
- Atoms are indivisible particles, which cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction.
- Atoms of any given element are identical in mass and chemical properties.
- Atoms of different elements have different masses and chemical properties.
- Atoms combine in the ratio of small whole numbers to form compounds.
- The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound.
Laws of Chemical Combination
Laws of Chemical Combination was suggested by Antoine L. Lavoisier. Laws of Chemical Combination have two parts, they are:-
- Law of Conservation of Mass
- Law of Constant proportions
Law of Conservation of Mass
The Law of Conservation of Mass states that mass of reactantes before the chemical reaction is equal to mass of products after the reaction.
Law of Constant proportions
The Law of Constant proportions states that atoms of different elements combined chemically in a fixed ratio.
Symbols for the elements
Dalton was the first scientist to use the symbols for elements.Further Berzilius suggested that the symbols of elements be made from one or two letters of the name of the element.
In the beginning, the names of elements were derived from the name of the place where they were found for the first time. For example, the name copper was taken from Cyprus.
Some names were taken from specific colours. For example, gold was taken from the English word meaning yellow.
Now-a-days, IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) approves names of elements. Many of the symbols are the first one or two letters of the element’s name in English. The first letter of a symbol is always written as a capital letter (uppercase) and the second letter as a small letter (lowercase)
| Name of element | Symbol of element |
| Aluminium | Al |
|---|---|
| Argon | Ar |
| Barium | Ba |
| Calcium | Ca |
| Carbon | C |
| Cobalt | Co |
| Fluorine | F |
| Copper | Cu |
| Gold | Au |
| Hydrogen | H |
| Iodine | I |
| Iron | Fe |
| Lead | Pb |
| Magnesium | Mg |
| Neon | Ne |
| Oxygen | O |
| Nitrogen | N |
| Potassium | K |
| Silicon | Si |
| Sodium | Na |
| Uranium | U |
| Zinc | Zn |
Atomic Mass
One atomic mass unit is a mass unit equal to exactly one-twelfth (1/12th) the mass of one atom of carbon-12.
The relative atomic masses of all elements have been found with respect to an atom of carbon-12.
Atomic mass of an atom of element states that how much times an atom of element is heavier than 1/12th of mass of one atom of carbon-12.
| Element | Atomic Mass (u) |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1 |
| Carbon | 12 |
| Nitrogen | 14 |
| Oxygen | 16 |
| Sodium | 23 |
| Magnesium | 24 |
| Sulphur | 32 |
| Chlorine | 35.5 |
| Calcium | 40 |
Molecules
Molecules are a group of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded together and tightly held together by attractive forces.An element or an compound that is capable of an independent existance and shows all the properties of that substance is known as molecule.
Molecules are made up of two or more similar or disimilar type of atoms.
Example:-Oxygen gas (O2) is composed of two similar kind of oxygen atoms and it exits in nature, so it is called (O2) gas molecule. Water is made up of two different kind of atoms (2 Hydrogen and 1 oxygen) and it exist in nature, so it is called ( H2O) molecules.
Molecules of Elements
Molecules of element can be monoatomic (composed of one atom, inert / noble gasses, (Helium - He, Argon - Ar, karpton - Kr, etc.), diatomic (composed of two atoms, (Oxygen - O2, Hydrogen - H2, Chlorine - Cl2, Nitrogen - N2, etc.) , triatomic (made up of three atoms like Ozone - O3) Tetra-atomic (composed of four atoms like Phosphorus - P4)
Atomicity
The total number of atoms constituting a molecules of an element or a compound is known as its atomicity.
Molecules of Compounds
| Compound | Combining Element | Atomcity | Ration by Mass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water (H2O) | Hydrogen, Oxygen | 2+1=3 | 1:8 |
| Ammonia (NH3) | Nitrogen, Hydrogen | 1+3=3 | 14:3 |
| Carbon Dioxide (CO2) | Carbon, Oxygen | 1+2=3 | 3:8 |
Ion
Ions are charged atoms/group of atoms. (+ve / -ve)
Compounds composed of metals and non- metals contain charged species. This charged species is known as Ion.
Ex:- Sodium atom losses an electron during chemical reaction and converted into sodium ion which is +ve. Similarly, Chlorine atom gains an electron and converted into chlorine ion which is -ve charged.
Ions are of two types:-
- +ve ion (Cation => Metal atoms ion)
- -ve ion (Anion => Non-metal atoms ion except inered gas)
In compound cations and anions held together by electrostatict force.
Name and symbols of some ions
| Valency | Name of ion | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sodium Potassium Silver Copper(Copurous) |
Na+ K+ Ag+ Cu+ |
| 2 | Magnesium Calcium Zinc Iron(Ferous) Copper(Copuric) |
Mg++ Ca++ Zn++ Fe++ Cu++ |
| 3 | Aluminium Iron(Ferric) |
Al+++ Fe+++ |
| Valency | Non-metallic element | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hydrogen Hydride Chloride Bromine Iodide |
H+ H- Cl- Br- I- |
| 2 | Oxide Sulphide |
O-- S-- |
| 3 | Nitride |
N-- |
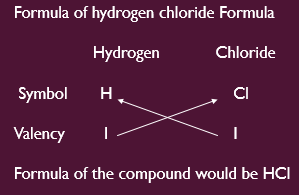
Writing Chemical Formulae
Binary compounds is the simplest compounds, which are made up of two different elements.
In order to write the chemical formulae for compounds, we write first the constituent elements in one row and their valencies in 2nd row just below of element symbol.
Molecular Mass
The molecular mass of any element or compund is the sum of the atomic masses of all constituent atoms .
Example:- Molecular mass of Sodium chloride (NaCl) = atomic mass of one atom of sodium + atomic mass of one atom of Chlorine. = 23 + 35.5 = 58.5u
Molecular mass of water (H2O) = atomic mass of two atom of hydrogen + atomic mass of one atom of oxygen. = (2 x 1) + (1 x 16) = 2 + 16 = 18u
Molecular mass of Sulphuric acid (H2SO4) = atomic mass of two atom of hydrogen + atomic mass of one atom of sulphur + atomic mass of four atom of oxygen. = (2 x 1) + (1 x 32) + (4 x 16) = 2 + 32 + 64 = 98u
Mole concept
The amount of substance containing 6.022 x 10²³ atoms / molecules is called one mole.
Mass of 1 mole of any substance is known as its molar mass.
12g of carbon-12 element contains 6.022 x 10²³ carbon atoms. Therefore molar mass of carbon-12 is 12g.
6.022 x 10²³ number was found by avagadro.So It is called Avogadro number.
The mass of 1 mole of any substance is equal to relative atomic mass of element or molecular mass of the compound.
The number of atoms in given quantity of element or compound = (mass of the element or molecules / molecular mass of element or molecules) x avagado number [6.022 x 10²³]
Example:- Calulate the number of atoms in 5g of calcium. (Given, atomic weight = 40u)
The number of atoms in 5g of calcium = (5g / 40g) x 6.022 x 10²³ = 7.5275 x 10²²
Related topics of CBSE Science class 9