Introduction
Mode of nutrition in plant
Autotrophic Nutrition
· Heterotrophic Nutrition
Autotrophic Nutrition
· The mode of nutrition in which organism synthesis or make their own food with the help of simple organic substances is called autotrophic nutrition.
· Such organisms are called autotrophs. They are also called producer.
· Example: - Green Plants etc.
Heterotrophic Nutrition
· The mode of nutrition in which organism obtain their food from plants and other animals is called heterotrophic nutrition.
· Such organisms are called heterotrophs.
· Example: - Human and non-green plant etc.
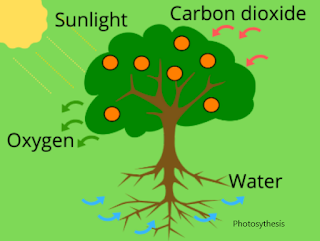
Photosynthesis — Food making process in plant
Chemical equation to describe the process of photosynthesis:
Carbon
dioxide + water —> carbohydrate + oxygen + water.
6CO2 + 6H2O
—> C6H12O6 (carbohydrate) + 6O2.
Photosynthesis uses light
energy to convert carbon dioxide into a carbohydrate in presence of chlorophyll.
· Carbon dioxide is taken through the tiny pores present on the surface of leaves. These pores are surrounded by ‘guard cell’. Such pores are called stomata.
· Conditions that are necessary for photosynthesis:
The
conditions necessary for photosynthesis to take place are:
- Sunlight
- Chlorophyll
- Carbon dioxide
- Water
Photosynthesis is important
It provides food for animals including human beings
It release oxygen gas into the air which is essential for breathing and respiration in animals & human beings.
Cells
·
The
smallest unit of any body is called as cell. It can be seen under microscope.
·
A
cell is capable of independently carrying out all necessary activities of
life such as nutrition, respiration, excretion, transportation. Therefore cell is called basic or functional unit of life.
·
They
are enclosed by cell membrane.
·
Spherical
structure at center is called the nucleus.
·
Jelly-like
substance near nucleus is called as cytoplasm.
Carbohydrate
·
Carbohydrates is the component of food .It is complex substances which cannot be utilized by the body. Therefore they are
broken down into simpler substances. The process of breaking down of complex
components of food into simpler substances is called digestion.
· Carbohydrates are made up of carbon, oxygen and hydrogen.
Carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins
and minerals are essential components of our food, these components are
known as nutrients.
Heterotrophic
Nutrition
· Some plants do not contain chlorophyll and cannot make their own food and are known as Heterotrophic plants.
· Such plants totally dependent
on other plants are called as parasites and the plants
on which parasites depend are called as hosts.
Insectivorous Plants
- Plants like pitcher plant and the Venus fly trap, insectivorous mode of nutrition is observed .
- These types of plants totally depend on other insects and small animals for their nutrition.
- Small insects are trapped by pitcher plants inside the pitcher and digested by the digestive juices secreted in the pitcher.
- Insectivorous plants grow well in the soils containing sufficient nitrogen mineral.
- These kind of plants are green and carry out photosynthesis to obtain a part of food.
Saprotrophs
- Saprotrophs are organisms that obtain nutrition from dead and decaying organic matter. Examples: Fungi and some bacteria.
- It is called saprotrophic nutrition.
Symbiosis
- Some organisms live together and share both food and shelter .This relation is called Symbiosis
- For example certain fungi live inside the root of plant, the plant provide nutrient to fungus and in return fungus provide water and some nutrient to plant.
- Lichen a chlorophyll containing partner, which is a alga and a fungus live together.
How nutrients are replenished in the soil?
- Plants are continuously taking nutrients from the soil in order to synthesize food. Due to this amount of nutrients in the soil decreases.
- Nutrients in the soil are replenished by adding fertilizers and manures.
- Fertilizers and manures contain plants nutrients and minerals like nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
- Another way to replenish soil ,We have to grow leguminous crops (for example gram, peas, pulses etc.) in the soil.
- The bacterium called Rhizobium can take atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into a soluble form.
- But Rhizobium cannot make its own food. So it lives in the roots of gram, peas, moong, beans and other legumes and provides them with nitrogen. In return plants provide food and shelter to the bacteria.